Circular dichroism
Circular dichroism (CD) refers to the differential absorption of left and right circularly polarized light.[1][2] This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century.[3] It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins.[4] UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions.[5] Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions.[2] Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.[4]
Contents |
Physical principles
Circular polarization of light
Electromagnetic radiation consists of an electric (E) and magnetic (B) field that oscillate perpendicular to one another and to the propagating direction.[6], a transverse wave. While linearly polarized light occurs when the electric field vector oscillates only in one plane, circularly polarized light occurs when the direction of the electric field vector rotates about its propagation direction while the vector retains constant magnitude. At a single point in space, the circularly polarized-vector will trace out a circle over one period of the wave frequency, hence the name. The two diagrams below show the electric vectors of linearly and circularly polarized light, at one moment of time, for a range of positions; the plot of the circularly polarized electric vector forms a helix along the direction of propagation (k). For left circularly polarized light (LCP) with propagation towards the observer, the electric vector rotates counterclockwise.[2] For right circularly polarized light (RCP), the electric vector rotates clockwise.
Interaction of circularly polarized light with matter
When circularly polarized light passes through an absorbing optically active medium, the speeds between right and left polarizations differ (cL ≠ cR) as well as their wavelength (λL ≠ λR) and the extent to which they are absorbed (εL≠εR). Circular dichroism is the difference Δε ≡ εL- εR.[4] The electric field of a light beam causes a linear displacement of charge when interacting with a molecule (electric dipole), whereas the magnetic field of it causes a circulation of charge (magnetic dipole). These two motions combined cause an excitation of an electron in a helical motion, which includes translation and rotation and their associated operators. The experimentally determined relationship between the rotational strength (R) of a sample and the Δε is given by
The rotational strength has also been determined theoretically,
We see from these two equations that in order to have non-zero 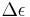 , the electric and magnetic dipole moment operators (
, the electric and magnetic dipole moment operators (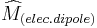 and
and 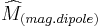 ) must transform as the same irreducible representation.
) must transform as the same irreducible representation. 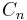 and
and 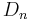 are the only point groups where this can occur, making only chiral molecules CD active.
are the only point groups where this can occur, making only chiral molecules CD active.
Simply put, since circularly polarized light itself is "chiral", it interacts differently with chiral molecules. That is, the two types of circularly polarized light are absorbed to different extents. In a CD experiment, equal amounts of left and right circularly polarized light of a selected wavelength are alternately radiated into a (chiral) sample. One of the two polarizations is absorbed more than the other one, and this wavelength-dependent difference of absorption is measured, yielding the CD spectrum of the sample. Due to the interaction with the molecule, the electric field vector of the light traces out an elliptical path after passing through the sample.
It is important that the chirality of the molecule can be conformational rather than structural. That is, for instance, a protein molecule with a helical secondary structure can have a CD that changes with changes in the conformation.
Delta absorbance
By definition,
where ΔA (Delta Absorbance) is the difference between absorbance of left circularly polarized (LCP) and right circularly polarized (RCP) light (this is what is usually measured). ΔA is a function of wavelength, so for a measurement to be meaningful the wavelength at which it was performed must be known.
Molar circular dichroism
It can also be expressed, by applying Beer's law, as:
where
- εL and εR are the molar extinction coefficients for LCP and RCP light,
- C is the molar concentration
- l is the path length in centimeters (cm).
Then
is the molar circular dichroism. This intrinsic property is what is usually meant by the circular dichroism of the substance. Since 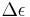 is a function of wavelength, a molar circular dichroism value (
is a function of wavelength, a molar circular dichroism value (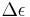 ) must specify the wavelength at which it is valid.
) must specify the wavelength at which it is valid.
Extrinsic effects on circular dichroism
In many practical applications of circular dichroism (CD), as discussed below, the measured CD is not simply an intrinsic property of the molecule, but rather depends on the molecular conformation. In such a case the CD may also be a function of temperature, concentration, and the chemical environment, including solvents. In this case the reported CD value must also specify these other relevant factors in order to be meaningful.
Molar ellipticity
Although ΔA is usually measured, for historical reasons most measurements are reported in degrees of ellipticity. Molar ellipticity is circular dichroism corrected for concentration. Molar circular dichroism and molar ellipticity, [θ], are readily interconverted by the equation:
This relationship is derived by defining the ellipticity of the polarization as:
where
- ER and EL are the magnitudes of the electric field vectors of the right-circularly and left-circularly polarized light, respectively.
When ER equals EL (when there is no difference in the absorbance of right- and left-circular polarized light), θ is 0° and the light is linearly polarized. When either ER or EL is equal to zero (when there is complete absorbance of the circular polarized light in one direction), θ is 45° and the light is circularly polarized.
Generally, the circular dichroism effect is small, so tanθ is small and can be approximated as θ in radians. Since the intensity or irradiance, I, of light is proportional to the square of the electric-field vector, the ellipticity becomes:
Then by substituting for I using Beer's law in natural logarithm form:
The ellipticity can now be written as:
Since ΔA << 1, this expression can be approximated by expanding the exponentials in a Taylor series to first-order and then discarding terms of ΔA in comparison with unity and converting from radians to degrees:
The linear dependence of solute concentration and pathlength is removed by defining molar ellipticity as,
Then combining the last two expression with Beer's law, molar ellipticity becomes:
The units of molar ellipticity are historically (deg·cm2/dmol). To calculate molar ellipticity, the sample concentration (g/L), cell pathlength (cm), and the molecular weight (g/mol) must be known.
If the sample is a protein, the mean residual weight (average molecular weight of the amino acids it contains) is used in place of the molecular weight, essentially treating the protein as a solution of amino acids.
Mean residue ellipticity
Methods for estimating secondary structure in polymers, proteins and polypeptides in particular, often require that the measured molar ellipticity spectrum be converted to a normalized value, specifically a value independent of the polymer length. Mean residue ellipticity is used for this purpose; it is simply the measured molar ellipticity of the molecule divided by the number of monomer units (residues) in the molecule.
Application to biological molecules
In general, this phenomenon will be exhibited in absorption bands of any optically active molecule. As a consequence, circular dichroism is exhibited by biological molecules, because of their dextrorotary and levorotary components. Even more important is that a secondary structure will also impart a distinct CD to its respective molecules. Therefore, the alpha helix of proteins and the double helix of nucleic acids have CD spectral signatures representative of their structures. The capacity of CD to give a representative structural signature makes it a powerful tool in modern biochemistry with applications that can be found in virtually every field of study.
CD is closely related to the optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) technique, and is generally considered to be more advanced. CD is measured in or near the absorption bands of the molecule of interest, while ORD can be measured far from these bands. CD's advantage is apparent in the data analysis. Structural elements are more clearly distinguished since their recorded bands do not overlap extensively at particular wavelengths as they do in ORD. In principle these two spectral measurements can be interconverted through an integral transform (Kramers–Kronig relation), if all the absorptions are included in the measurements.
The far-UV (ultraviolet) CD spectrum of proteins can reveal important characteristics of their secondary structure. CD spectra can be readily used to estimate the fraction of a molecule that is in the alpha-helix conformation, the beta-sheet conformation, the beta-turn conformation, or some other (e.g. random coil) conformation.[7][8] These fractional assignments place important constraints on the possible secondary conformations that the protein can be in. CD cannot, in general, say where the alpha helices that are detected are located within the molecule or even completely predict how many there are. Despite this, CD is a valuable tool, especially for showing changes in conformation. It can, for instance, be used to study how the secondary structure of a molecule changes as a function of temperature or of the concentration of denaturing agents, e.g. Guanidinium hydrochloride or urea. In this way it can reveal important thermodynamic information about the molecule (such as the enthalpy and Gibbs free energy of denaturation) that cannot otherwise be easily obtained. Anyone attempting to study a protein will find CD a valuable tool for verifying that the protein is in its native conformation before undertaking extensive and/or expensive experiments with it. Also, there are a number of other uses for CD spectroscopy in protein chemistry not related to alpha-helix fraction estimation.
The near-UV CD spectrum (>250 nm) of proteins provides information on the tertiary structure. The signals obtained in the 250–300 nm region are due to the absorption, dipole orientation and the nature of the surrounding environment of the phenylalanine, tyrosine, cysteine (or S-S disulfide bridges) and tryptophan amino acids. Unlike in far-UV CD, the near-UV CD spectrum cannot be assigned to any particular 3D structure. Rather, near-UV CD spectra provide structural information on the nature of the prosthetic groups in proteins, e.g., the heme groups in hemoglobin and cytochrome c.
Visible CD spectroscopy is a very powerful technique to study metal–protein interactions and can resolve individual d–d electronic transitions as separate bands. CD spectra in the visible light region are only produced when a metal ion is in a chiral environment, thus, free metal ions in solution are not detected. This has the advantage of only observing the protein-bound metal, so pH dependence and stoichiometries are readily obtained. Optical activity in transition metal ion complexes have been attributed to configurational, conformational and the vicinal effects. Klewpatinond and Viles (2007) have produced a set of empirical rules for predicting the appearance of visible CD spectra for Cu2+ and Ni2+ square-planar complexes involving histidine and main-chain coordination.
CD gives less specific structural information than X-ray crystallography and protein NMR spectroscopy, for example, which both give atomic resolution data. However, CD spectroscopy is a quick method that does not require large amounts of proteins or extensive data processing. Thus CD can be used to survey a large number of solvent conditions, varying temperature, pH, salinity, and the presence of various cofactors.
CD spectroscopy is usually used to study proteins in solution, and thus it complements methods that study the solid state. This is also a limitation, in that many proteins are embedded in membranes in their native state, and solutions containing membrane structures are often strongly scattering. CD is sometimes measured in thin films.
Experimental limitations
CD has also been studied in carbohydrates, but with limited success due to the experimental difficulties associated with measurement of CD spectra in the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) region of the spectrum (100–200 nm), where the corresponding CD bands of unsubstituted carbohydrates lie. Substituted carbohydrates with bands above the VUV region have been successfully measured.
Measurement of CD is also complicated by the fact that typical aqueous buffer systems often absorb in the range where structural features exhibit differential absorption of circularly polarized light. Phosphate, sulfate, carbonate, and acetate buffers are generally incompatible with CD unless made extremely dilute e.g. in the 10–50 mM range. The TRIS buffer system should be completely avoided when performing far-UV CD. Borate and Onium compounds are often used to establish the appropriate pH range for CD experiments. Some experimenters have substituted fluoride for chloride ion because fluoride absorbs less in the far UV, and some have worked in pure water. Another, almost universal, technique is to minimize solvent absorption by using shorter path length cells when working in the far UV, 0.1 mm path lengths are not uncommon in this work.
In addition to measuring in aqueous systems, CD, particularly far-UV CD, can be measured in organic solvents e.g. ethanol, methanol, trifluoroethanol (TFE). The latter has the advantage to induce structure formation of proteins, inducing beta-sheets in some and alpha helices in others, which they would not show under normal aqueous conditions. Most common organic solvents such as acetonitrile, THF, chloroform, dichloromethane are however, incompatible with far-UV CD.
It may be of interest to note that the protein CD spectra used in secondary structure estimation are related to the π to π* orbital absorptions of the amide bonds linking the amino acids. These absorption bands lie partly in the so-called vacuum ultraviolet (wavelengths less than about 200 nm). The wavelength region of interest is actually inaccessible in air because of the strong absorption of light by oxygen at these wavelengths. In practice these spectra are measured not in vacuum but in an oxygen-free instrument (filled with pure nitrogen gas).
Once oxygen has been eliminated, perhaps the second most important technical factor in working below 200 nm is to design the rest of the optical system to have low losses in this region. Critical in this regard is the use of aluminized mirrors whose coatings have been optimized for low loss in this region of the spectrum.
The usual light source in these instruments is a high pressure, short-arc xenon lamp. Ordinary xenon arc lamps are unsuitable for use in the low UV. Instead, specially constructed lamps with envelopes made from high-purity synthetic fused silica must be used.
Light from synchrotron sources has a much higher flux at short wavelengths, and has been used to record CD down to 160 nm. Recently the CD spectrometer at the electron storage ring facility ISA at the University of Aarhus in Denmark was used to record solid state CD spectra down to 120 nm.[9] At the quantum mechanical level, the information content of circular dichroism and optical rotation are identical.
See also
References
- ^ P. Atkins and J. de Paula (2005). Elements of Physical Chemistry, 4th ed.. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0716773295.
- ^ a b c Edward I. Solomon; A. B. P. Lever (3 February 2006). Inorganic electronic structure and spectroscopy. Wiley-Interscience. p. 78. ISBN 9780471971245. http://books.google.com/books?id=C7KaQgAACAAJ. Retrieved 29 April 2011.
- ^ Gerald D. Fasman (1996). Circular dichroism and the conformational analysis of biomolecules. Springer. pp. 3–. ISBN 9780306451423. http://books.google.com/books?id=ivc0FaowEYMC&pg=PA3. Retrieved 29 April 2011.
- ^ a b c Kōji Nakanishi; Nina Berova; Robert Woody (1994). Circular dichroism: principles and applications. VCH. p. 473. ISBN 9781560816188. http://books.google.com/books?id=aNWjQgAACAAJ. Retrieved 29 April 2011.
- ^ Solomon, Neidig; A. T. Wecksler, G. Schenk, and T. R. Holman (2007). "Kinetic and Spectroscopic Studies of N694C Lipoxygenase: A Probe of the Substrate Activation Mechanism of a Nonheme Ferric Enzyme". J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 129 (24): 7531–7537. doi:10.1021/ja068503d. PMC 2896304. PMID 17523638. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2896304.
- ^ Alison Rodger; Bengt Nordén (1997). Circular dichroism and linear dichroism. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198558972. http://books.google.com/books?id=THeKGC99hJcC. Retrieved 29 April 2011.
- ^ Whitmore L, Wallace BA (2008). "Protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopy: methods and reference databases". Biopolymers 89 (5): 392–400. doi:10.1002/bip.20853. PMID 17896349.
- ^ Greenfield NJ (2006). "Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure". Nature protocols 1 (6): 2876–90. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.202. PMC 2728378. PMID 17406547. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2728378.
- ^ U. Meierhenrich, J.J. Filippi, C. Meinert, J. H. Bredehöft, J. Takahashi, L. Nahon, N. C. Jones, S. V. Hoffmann (2010). "Circular Dichroism of Amino Acids in the Vacuum-Ultraviolet Region.". Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed. 49 (42): 7799–7802. doi:10.1002/anie.201003877. PMID 20845349.
External links
- Circular Dichroism explained
- Circular Dichroism at UMDNJ – a good site for information on structure estimation software [broken link]
- Electromagnetic waves – Animated electromagnetic waves. The Emanim program is a teaching resource for helping students understand the nature of electromagnetic waves and their interaction with birefringent and dichroic samples
- An Introduction to Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy – a very good tutorial on circular dichroism spectroscopy
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
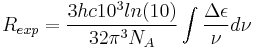
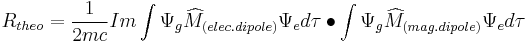
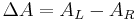
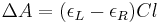
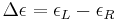
![[\theta] = 3298.2\,\Delta \varepsilon.\,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/250d867271d800797c1bc1f1aa1e9ef6.png)
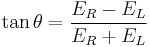
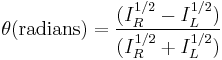
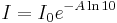
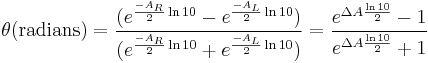
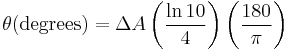
![[\theta] = \frac {100\theta}{\text{Cl}}\,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/89d17fd80a61a27bce2cad862d9220d5.png)
![[\theta]= 100 \,\Delta \varepsilon \left( \frac {\ln 10}{4} \right) \left( \frac {180}{\pi} \right) = 3298.2\,\Delta \varepsilon \,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/447c5c641ccd6cef8ba87d40ba1483fa.png)